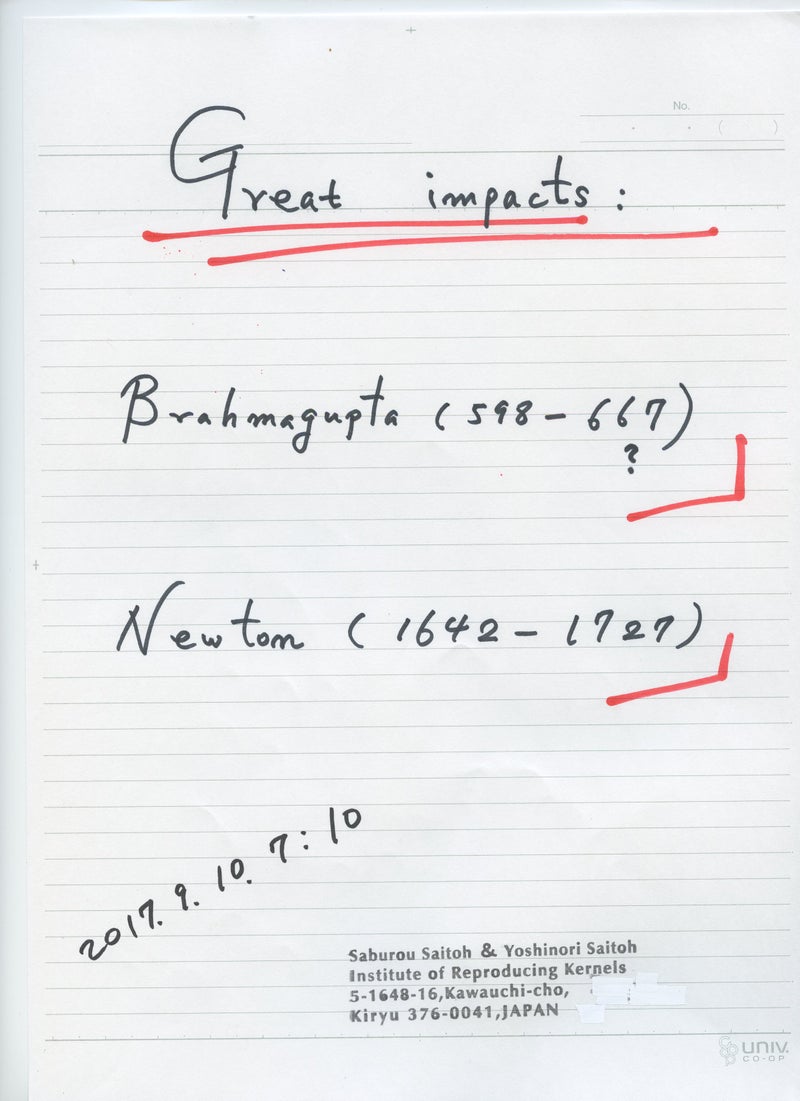中国皇帝首次接见的数学家竟然是资阳人 “科学史之父”都说他伟大!
四川在线资阳频道消息(记者李秋君)有着“科学史之父”之称的美国科学史家萨顿高度评价秦九韶:“他那个民族、他那个时代、并且确实也是所有时代最伟大的数学家之一。”

秦九韶广场内的秦九韶雕像
守孝期间,完成二十多万字的数学巨著,凭借自己在数学、天文历法等方面的丰富知识及成就成为中国历史上第一位受皇帝接见的中国数学家。
秦九韶到底是谁?
他为人类历史的进步做了哪些贡献?
他和资阳有怎样的联系?
秦九韶(1208—1268),字道古,出生于普州(今资阳安岳)天庆观街“秦苑斋”的一个书香门第,官宦世家。为母守孝期间,写成了影响世界的数学巨著《数书九章》,提出的正负开方术(秦九韶法)以及一次同余组解法(大衍求一术,西方称“中国剩余定理”),代表了中世纪世界数学发展的主流与最高水平。

秦九韶纪念馆正殿
普州“三秦”祖孙三代三进士6岁秦九韶就会“造楼”
1208年春,秦九韶就出生在普州(资阳安岳县),并在此度过了无忧无虑的少儿时代。
秦九韶的祖父秦臻舜,绍兴三十年进士(当时最高学历)及第,官至通议大夫(正四品)。其父亲名叫秦季栖,绍熙四年(1193)与南宋哲学家陈亮、程璐一起参加科举考试,成为同榜进士。
正是出生于官宦之家、不断接受着忠臣良相的熏陶,秦九韶自小便聪明伶俐,极富想象力和创造力。
普州民间传说记载,在秦九韶6岁的一天,秦九韶的老师和秦夫人带他去大云山栖岩寺,恰好碰上朝圣。当秦九韶走到栖岩寺西侧的飞鹤楼下,却久久不肯离去,母亲便先去到佛殿。
飞鹤楼建在大云山栖岩寺的西侧,七层八角,高达八丈,布局严谨。在飞鹤楼驻足片刻,秦九韶突然向前山跑去,不一会儿,便抱回一大捆茅杆,在飞鹤楼前用茅杆模仿造飞鹤楼。他越造越兴奋,越造越离奇,一座比秦九韶还高,酷似飞鹤楼的模型完成。
幼时的聪慧,让秦九韶注定不凡。据记载,在其父亲任职工部郎中和秘书少监期间,秦九韶一有机会就阅读大量典籍,并拜访天文历法和建筑等方面的专家,请教天文历法和土木工程问题,甚至深入工地,了解施工情况。逐渐,他便成为了一位学识渊博、多才多艺的青年学者,时人说他“性极机巧,星象、音律、算术,以至营造等事,无不精究。”
《宋史》记载,绍定四年(1231年),宋理宗策试天下贡士,秦九韶等493人进士及弟。自此,普州“三秦”祖孙三代三进士。

秦九韶纪念馆正殿和右侧大厅
“大孝子”不忘体恤民情 “父母官”亲力亲为做事
秦九韶祖籍山东,出生于四川,在其父调任首都临安(杭州),全家住在西溪河畔。而临安的一场大火,烧了三天三夜,烧掉太庙、三省、六部、御史台等,受灾居民达三万五千多家,部分朝廷命官及家眷便迁居当时属于郊外的西溪河畔,秦家来杭州后也住那里。
而在杭州西溪路上曾经有一座老桥,叫道古桥。始建于南宋嘉熙年间(1237-1241),初名西溪桥。南宋咸淳初年《临安志》有载:“‘西溪桥’,本府试院东,宋代嘉熙年间道古建造。”
这个造桥的“道古”不是别人,正是南宋大数学家秦九韶,道古是他的字。
1231年秦九韶考中进士,先后在湖北、安徽、江苏、广东等地为官。1238年,秦九韶回临安为父奔丧,见河上无桥,两岸人民往来很不便,便亲自设计,再通过朋友从府库得到银两资助,在西溪河上造了这座桥。桥建好后,原本没有名字,因桥建在西溪河上,习惯上被叫作“西溪桥”。
直到元代初年,另一位大数学家、游历四方的北方人朱世杰(1249-1314)来到杭州,倡议将“西溪桥”更名“道古桥”,以纪念造桥人、他所敬仰的前辈数学家秦九韶,并亲自将桥名书镌桥头。
道古桥一直存在到新千年之交,因为西溪路扩建改造,旧桥拆平,建起高楼大厦,只留一个公交车站,名道古桥。
秦九韶造桥的故事,堪与牛顿造桥的故事媲美。现今剑桥大学皇后学院内,流经的剑河上有一座桥叫数学桥,传说原桥设计师是17世纪的数学家牛顿。据称牛顿造桥时没用一枚钉子,后来有好事者悄悄把桥拆下来,发现真是这样,却再也无法安装回去,只好在原址重新造了一座桥。数学桥至今仍是一处名胜,是到访剑桥旅客的必游之地。相比之下,道古桥的故事不仅更为古老,且与两位中国古代大数学家有关。
化“悲愤为力量 ” 创“数学世界”最高水平
1244年,秦九韶任建康府(南京)通判期间,因母丧离任,回浙江湖州守孝三年。正是在湖州守孝期间,秦九韶专心研究数学,完成了二十多万字的巨著《数书九章》(1247),名声大振。加上他在天文历法方面的丰富知识和成就,曾受皇帝(宋理宗赵昀)召见。他在皇帝面前阐述自己的见解,并呈奏书稿“数学大略”(即《数书九章》)。可以说,秦九韶是第一个受皇帝接见的中国数学家。

安岳秦九韶广场镌刻的秦九韶《数书九章》序全文
《数书九章》分九卷(类),每类九个问题,其中最重要的成果无疑要数第一卷里的“大衍总数术” 。
秦九韶发现的定理当时的用途并非在理论上,而主要用于解决历法、工程、赋役和军旅等实际问题。1801年,数学王子高斯的名著《算术研究》,也给出了上述结果,但他不知道中国的数学家早已经有这个结论。直到1852年,秦九韶的结果和方法被英国传教士伟烈亚力译介到欧洲,并被迅速从英文转译成德文和法文,引起了广泛关注。
严格来讲,孙子定理应称为孙子—秦九韶定理,或秦九韶定理,这一定理被西方人称之为“中国剩余定理”。据先师潘承洞教授分析,西方人之所以下此定义,是因为古代中国数学家注重计算,缺乏理论建树,因而是一种轻视。无论如何,它都可以说是中国人发现的最具世界性影响的定理,是中外任何一本基础数论教科书不可或缺的。在新近由高等教育出版社出版的拙著《数之书》中,首次依照国际惯例命名为“秦九韶定理”。
2005年,牛津大学出版社出版了《数学史,从美索不达米亚到现代》,该书内容提要仅提及12位数学家,秦九韶是唯一的中国人。而新近由BBC制作的四集纪录片《数学的故事》中有17分钟谈论中国数学,秦九韶也是唯一提到的数学家。
此外,《数书九章》第九卷“市易类”的“正负开方术”,也非常重要。“正负开方术”也可称“秦九韶算法”,给出了一般n次代数方程正根的解法,系数可正可负。即便在计算机时代的今天,“秦九韶算法”仍有重要的意义。(新闻热线:028-26221630 微信爆料:ziyangscol)http://sichuan.scol.com.cn/zyxw/201709/55999843.html
とても興味深く読みました:中国はゼロ除算は・・・・・・・・
再生核研究所声明353(2017.2.2) ゼロ除算 記念日
2014.2.2 に 一般の方から100/0 の意味を問われていた頃、偶然に執筆中の論文原稿にそれがゼロとなっているのを発見した。直ぐに結果に驚いて友人にメールしたり、同僚に話した。それ以来、ちょうど3年、相当詳しい記録と経過が記録されている。重要なものは再生核研究所声明として英文と和文で公表されている。最初のものは
再生核研究所声明 148(2014.2.12): 100/0=0, 0/0=0 - 割り算の考えを自然に拡張すると ― 神の意志
で、最新のは
Announcement 352 (2017.2.2): On the third birthday of the division by zero z/0=0
である。
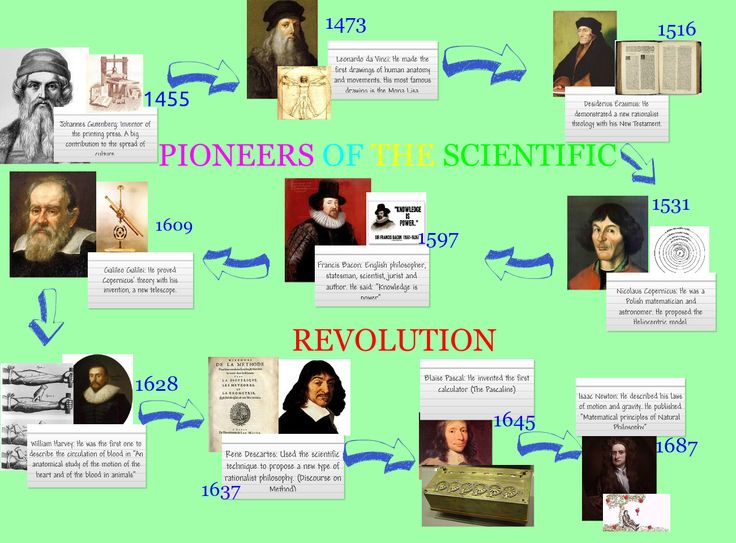
アリストテレス、ブラーマグプタ、ニュートン、オイラー、アインシュタインなどが深く関与する ゼロ除算の神秘的な永い歴史上の発見であるから、その日をゼロ除算記念日として定めて、世界史を進化させる決意の日としたい。ゼロ除算は、ユークリッド幾何学の変更といわゆるリーマン球面の無限遠点の考え方の変更を求めている。― 実際、ゼロ除算の歴史は人類の闘争の歴史と共に 人類の愚かさの象徴であるとしている。
心すべき要点を纏めて置きたい。
1) ゼロの明確な発見と算術の確立者Brahmagupta (598 - 668 ?) は 既にそこで、0/0=0 と定義していたにも関わらず、言わば創業者の深い考察を理解できず、それは間違いであるとして、1300年以上も間違いを繰り返してきた。
2) 予断と偏見、慣習、習慣、思い込み、権威に盲従する人間の精神の弱さ、愚かさを自戒したい。我々は何時もそのように囚われていて、虚像を見ていると 真智を愛する心を大事にして行きたい。絶えず、それは真かと 問うていかなければならない。
3) ピタゴラス派では 無理数の発見をしていたが、なんと、無理数の存在は自分たちの世界観に合わないからという理由で、― その発見は都合が悪いので ― 、弟子を処刑にしてしまったという。真智への愛より、面子、権力争い、勢力争い、利害が大事という人間の浅ましさの典型的な例である。
4) この辺は、2000年以上も前に、既に世の聖人、賢人が諭されてきたのに いまだ人間は生物の本能レベルを越えておらず、愚かな世界史を続けている。人間が人間として生きる意義は 真智への愛にある と言える。
5) いわば創業者の偉大な精神が正確に、上手く伝えられず、ピタゴラス派のような対応をとっているのは、本末転倒で、そのようなことが世に溢れていると警戒していきたい。本来あるべきものが逆になっていて、社会をおかしくしている。
6) ゼロ除算の発見記念日に 繰り返し、人類の愚かさを反省して、明るい世界史を切り拓いて行きたい。
以 上
追記:
The division by zero is uniquely and reasonably determined as 1/0=0/0=z/0=0 in the natural extensions of fractions. We have to change our basic ideas for our space and world:
Division by Zero z/0 = 0 in Euclidean Spaces
Hiroshi Michiwaki, Hiroshi Okumura and Saburou Saitoh
International Journal of Mathematics and Computation Vol. 28(2017); Issue 1, 2017), 1-16.
http://www.scirp.org/journal/alamt http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/alamt.2016.62007
http://www.ijapm.org/show-63-504-1.html
http://www.diogenes.bg/ijam/contents/2014-27-2/9/9.pdf
http://www.ijapm.org/show-63-504-1.html
http://www.diogenes.bg/ijam/contents/2014-27-2/9/9.pdf
再生核研究所声明371(2017.6.27)ゼロ除算の講演― 国際会議 https://sites.google.com/site/sandrapinelas/icddea-2017 報告
http://ameblo.jp/syoshinoris/theme-10006253398.html
1/0=0、0/0=0、z/0=0
http://ameblo.jp/syoshinoris/entry-12276045402.html
1/0=0、0/0=0、z/0=0
http://ameblo.jp/syoshinoris/entry-12263708422.html
1/0=0、0/0=0、z/0=0
http://ameblo.jp/syoshinoris/entry-12272721615.html
再生核研究所声明325(2016.10.14) ゼロ除算の状況について ー 研究・教育活動への参加を求めて
アリストテレス以来、あるいは西暦628年インドにおけるゼロの記録と、算術の確立以来、またアインシュタインの人生最大の懸案の問題とされてきた、ゼロで割る問題 ゼロ除算は、本質的に新しい局面を迎え、数学における初歩的な部分の欠落が明瞭になってきた。ここ70年を越えても教科書や学術書における数学の初歩的な部分の期待される変更は かつて無かった事である。ユークリッドの考えた空間と解析幾何学などで述べられる我々の空間は実は違っていた。いわゆる非ユークリッド空間とも違う空間が現れた。不思議な飛び、ワープ現象が起きている世界である。ゼロと無限の不思議な関係を述べている。これが我々の空間であると考えられる。
そこで、最近の成果を基に現状における学術書、教科書の変更すべき大勢を外観して置きたい。特に、大学学部までの初等数学において、日本人の寄与は皆無であると言えるから、ゼロ除算の教育、研究は日本人が数学の基礎に貢献できる稀なる好機にもなるので、数学者、教育者など関係者の協力、参加をお願いしたい。
先ず、数学の基礎である四則演算において ゼロでは割れない との世の定説を改め、自然に拡張された分数、割り算で、いつでも四則演算は例外なく、可能であるとする。数学はより美しく、完全であった。さらに、数学の奥深い世界を示している。ゼロ除算を含む体の構造、山田体が確立している。その考えは、殆ど当たり前の従来の演算の修正であるが、分数における考え方に新規で重要、面白い、概念がある。その際、小学生から割り算や分数の定義を除算の意味で 繰り返し減法(道脇方式)で定義し、ゼロ除算は自明であるとし 計算機が割り算を行うような算法で 計算方法も指導する。― この方法は割り算の簡明な算法として児童・生徒たちにも歓迎されるだろう。
反比例の法則や関数y=1/xの出現の際には、その原点での値はゼロであると 定義する。その広範な応用は 学習過程の進展に従って どんどん触れて行くこととする。応用する。
いわゆるユークリッド幾何学の学習においては、立体射影の概念に早期に触れ、ゼロ除算が拓いた新しい空間像を指導する。無限、無限の彼方の概念、平行線の概念、勾配の概念を変える必要がある。どのように、如何に、カリキュラムに取り組むかは、もちろん、慎重な検討が必要で、数学界、教育界などの関係者による国家的取り組み、協議が必要である。重要項目は、直交座標系で y軸の勾配はゼロであること。真無限における破壊現象、接線などの新しい性質、解析幾何学との美しい関係と調和。すべての直線が原点を代数的に通り、平行な2直線は原点で代数的に交わっていること。行列式と破壊現象の美しい関係など。三角関数や初等関数でも考え方を修正、補充する。直線とは、そもそも、従来の直線に原点を加えたもので、平行線の公理は実は成り立たず、我々の世界は、ユークリッド空間でも、いわゆる非ユークリッド幾何学でもない、新しい空間である。原点は、あらゆる直線の中心になっている。
大学レベルになれば、微積分、線形代数、微分方程式、複素解析をゼロ除算の発展の成果で修正、補充して行く。複素解析学におけるローラン展開の学習以前でも形式的なローラン展開(負べき項を含む展開)の中心の値をゼロ除算で定義し ― ゼロ除算算法、広範な応用を展開する。最も顕著な例は、tan 90度 の値がゼロであることで、いろいろ幾何学的な説明は、我々の空間の認識を変えるのに教育的で楽しい題材である。特に微分係数が正や負の無限大に収束(発散)する時、微分係数をゼロと修正することによって、微分法の多くの公式や定理の表現が簡素化され、教科書の結構な記述の変更が要求される。媒介変数を含む多くの関数族は、ゼロ除算 算法で統一的な視点が与えられる。多くの公式の記述が簡単になり、修正される。新しい、関数の素性が見えてくる。
複素解析学において 無限遠点はゼロで表現されると、コペルニクス的変更(無限とされていたのが実はゼロだった)を行い、極の概念を次のように変更する。極、特異点の定義は そのままであるが、それらの点の近傍で、限りなく無限の値に近づく値を位数まで込めて取るが、特異点自身では、ゼロ除算に言う、有限確定値をとるとする。その有限確定値のいろいろ幾何学的な意味を学ぶ。古典的な鏡像の定説;原点の 原点を中心とする円に関する鏡像は無限遠点であるは、誤りであり、修正し、ゼロであると いろいろな根拠によって説明する。これら、無限遠点の考え方の修正は、ユークリッド以来、我々の空間に対する認識の世界史上における大きな変更であり、数学を越えた世界観の変更を意味している。これはアリストテレスの世界の連続性の概念を変えるもので強力な不連続性を示している。 ― この文脈では天動説が地動説に変わった歴史上の事件が想起される。
ゼロ除算は 物理学を始め、広く自然科学や計算機科学への大きな影響があり、さらに哲学、宗教、文化への大きな影響がある。しかしながら、ゼロ除算の研究成果を教科書、学術書に遅滞なく取り入れていくことは、真智への愛、真理の追究の表現であり、四則演算が自由にできないとなれば、数学者ばかりではなく、人類の名誉にも関わることである。実際、ゼロ除算の歴史は 止むことのない闘争の歴史とともに人類の恥ずべき人類の愚かさの象徴となるだろう。世間ではゼロ除算について不適切な情報が溢れていて 今尚奇怪で抽象的な議論によって混乱していると言える。― 美しい世界が拓けているのに、誰がそれを閉ざそうと、隠したいと、無視したいと考えられるだろうか。我々は間違いを含む、不適切な数学を教えていると言える: ― 再生核研究所声明 41: 世界史、大義、評価、神、最後の審判 ―。
地動説のように真実は、実体は既に明らかである。 ― 研究と研究成果の活用の推進を 大きな夢を懐きながら 要請したい。 研究課題は基礎的で関与する分野は広い、いろいろな方の研究・教育活動への参加を求めたい。素人でも数学の研究に参加できる新しい初歩的な数学を沢山含んでいる。ゼロ除算は発展中の世界史上の事件、問題であると言える。
以 上
追記:
http://www.diogenes.bg/ijam/contents/2014-27-2/9/9.pdf DOI:10.12732/ijam.v27i2.9.
*156 Qian,T./Rodino,L.(eds.): Mathematical Analysis, Probability and
Applications -Plenary Lectures: Isaac 2015, Macau, China.
(Springer Proceedings in Mathematics and Statistics, Vol. 177) Sep. 2016 305 pp. (Springer)
Paper:Division by Zero z/0 = 0 in Euclidean Spaces
Dear Prof. Hiroshi Michiwaki, Hiroshi Okumura and Saburou Saitoh
With reference to above, The Editor-in-Chief IJMC (Prof. Haydar Akca) accepted the your paper after getting positive and supporting respond from the reviewer.
Now, we inform you that your paper is accepted for next issue of International Journal of Mathematics and Computation 9 Vol. 28; Issue 1, 2017),
数学基礎学力研究会のホームページ
URLは
再生核研究所声明368(2017.5.19)ゼロ除算の意義、本質
ゼロ除算の本質、意義について、既に述べているが、参照すると良くまとめられているので、初めに復習して、新しい視点を入れたい。
再生核研究所声明359(2017.3.20) ゼロ除算とは何か ― 本質、意義
ゼロ除算の理解を進めるために ゼロ除算とは何か の題名で、簡潔に表現して置きたい。 構想と情念、想いが湧いてきたためである。
基本的な関数y=1/x を考える。 これは直角双曲線関数で、原点以外は勿論、値、関数が定義されている。問題はこの関数が、x=0 で どうなっているかである。結論は、この関数の原点での値を ゼロと定義する ということである。 定義するのである。定義であるから勝手であり、従来の定義や理論に反しない限り、定義は勝手であると言える。原点での値を明確に定義した理論はないから、この定義は良いと考えられる。それを、y=1/0=0 と記述する。ゼロ除算は不可能であるという、数学の永い定説に従って、1/0 の表記は学術書、教科書にもないから、1/0=0 の記法は 形式不変の原理、原則 にも反しないと言える。― 多くの数学者は注意深いから、1/0=\infty の表記を避けてきたが、想像上では x が 0 に近づいたとき、限りなく 絶対値が大きくなるので、複素解析学では、表現1/0=\infty は避けても、1/0=\infty と考えている事は多い。(無限大の記号がない時代、アーベルなどもそのような記号を用いていて、オイラーは1/0=\inftyと述べ、それは間違いであると指摘されてきた。 しかしながら、無限大とは何か、数かとの疑問は 続いている。)。ここが大事な論点である。近づいていった極限値がそこでの値であろうと考えるのは、極めて自然な発想であるが、現代では、不連続性の概念 が十分確立されていて、極限値がそこでの値と違う例は、既にありふれている。― アリストテレスは 連続性の世界観をもち、特にアリストテレスの影響を深く受けている欧米の方は、この強力な不連続性を中々受け入れられないようである。無限にいくと考えられてきたのが突然、ゼロになるという定義になるからである。 しかしながら、関数y=1/xのグラフを書いて見れば、原点は双曲線のグラフの中心の点であり、美しい点で、この定義は魅力的に見えてくるだろう。
定義したことには、それに至るいろいろな考察、経過、動機、理由がある。― 分数、割り算の意味、意義、一意性問題、代数的な意味づけなどであるが、それらは既に数学的に確立しているので、ここでは触れない。
すると、定義したからには、それがどのような意味が存在して、世の中に、数学にどのような影響があるかが、問題になる。これについて、現在、初等数学の学部レベルの数学をゼロ除算の定義に従って、眺めると、ゼロ除算、すなわち、 分母がゼロになる場合が表現上現れる広範な場合に 新しい現象が発見され、ゼロ除算が関係する広範な場合に大きな影響が出て、数学は美しく統一的に補充,完全化されることが分かった。それらは現在、380件以上のメモにまとめられている。しかしながら、世界観の変更は特に重要であると考えられる:
複素解析学で無限遠点は その意味で1/0=0で、複素数0で表されること、アリストテレスの連続性の概念に反し、ユークリッド空間とも異なる新しい空間が 現れている。直線のコンパクト化の理想点は原点で、全ての直線が原点を含むと、超古典的な結果に反する。更に、ゼロと無限の関係が明らかにされてきた。
ゼロ除算は、現代数学の初等部分の相当な変革を要求していると考えられる。
以 上
ゼロ除算の代数的な意義は、山田体の概念で体にゼロ除算を含む構造の入れ方、一般に体にゼロ除算の概念が入れられるが、代数的な発展については 専門外で、触れられない。ただ、計算機科学でゼロ除算と代数的な構造について相当議論している研究者がいる。
ゼロ除算の解析学的な意義は、従来孤立特異点での研究とは、孤立点での近傍での研究であり、正確に述べれば 孤立特異点そのものでの研究はなされていないと考えられる。
なぜならば、特異点では、ゼロ分のとなり、分子がゼロの場合には ロピタルの定理や微分法の概念で 極限値で考えてきたが、ゼロ除算は、一般に分子がゼロでない場合にも意味を与え、極限値でなくて、特異点で 何時でも有限確定値を指定できる ― ゼロ除算算法。初めて、特異点そのものの世界に立ち入ったと言える。従来は孤立特異点を除いた世界で 数学を考えてきたと言える。その意味でゼロ除算は 全く新しい数学、世界であると言える。典型的な結果は tan(\pi/2) =0で、y軸の勾配がゼロであることである。
ゼロ除算の幾何学的な意義は、ユークリッド空間のアレクサンドロフの1点コンパクト化に、アリストテレスの連続性の概念でない、強力な不連続性が現れたことで、全く新しい空間の構造が現れ、幾何学の無限遠点に関係する部分に全く新規な世界が現れたことである。所謂無限遠点が数値ゼロで、表現される。
さらに、およそ無限量と考えられたものが、実は、数値ゼロで表現されるという新しい現象が発見された。tan(\pi/2) =0の意味を幾何学的に考えると、そのことを表している。これはいろいろな恒等式に新しい要素を、性質を顕にしている。ゼロが、不可能性を表現したり、基準を表すなど、ゼロの意義についても新しい概念が現れている。
以 上
再生核研究所声明312(2016.07.14) ゼロ除算による 平成の数学改革を提案する
アリストテレス以来、あるいは西暦628年インドにおけるゼロの記録と、算術の確立以来、またアインシュタインの人生最大の懸案の問題とされてきた、ゼロで割る問題 ゼロ除算は、本質的に新しい局面を迎え、数学における基礎的な部分の欠落が明瞭になってきた。ここ70年を越えても教科書や学術書における数学の基礎的な部分の変更は かつて無かった事である。
そこで、最近の成果を基に現状における学術書、教科書の変更すべき大勢を外観して置きたい。特に、大学学部までの初等数学において、日本人の寄与は皆無であると言えるから、日本人が数学の基礎に貢献できる稀なる好機にもなるので、数学者、教育者など関係者の注意を換気したい。― この文脈では稀なる日本人数学者 関孝和の業績が世界の数学に活かせなかったことは 誠に残念に思われる。
先ず、数学の基礎である四則演算において ゼロでは割れない との世の定説を改め、自然に拡張された分数、割り算で、いつでも四則演算は例外なく、可能であるとする。山田体の導入。その際、小学生から割り算や分数の定義を除算の意味で 繰り返し減法(道脇方式)で定義し、ゼロ除算は自明であるとし 計算機が割り算を行うような算法で 計算方法も指導する。― この方法は割り算の簡明な算法として児童に歓迎されるだろう。
反比例の法則や関数y=1/xの出現の際には、その原点での値はゼロであると 定義する。その広範な応用は 学習過程の進展に従って どんどん触れて行くこととする。
いわゆるユークリッド幾何学の学習においては、立体射影の概念に早期に触れ、ゼロ除算が拓いた新しい空間像を指導する。無限、無限の彼方の概念、平行線の概念、勾配の概念を変える必要がある。どのように、如何に、カリキュラムに取り組むかは、もちろん、慎重な検討が必要で、数学界、教育界などの関係者による国家的取り組み、協議が必要である。重要項目は、直角座標系で y軸の勾配はゼロであること。真無限における破壊現象、接線などの新しい性質、解析幾何学との美しい関係と調和。すべての直線が原点を代数的に通り、平行な2直線は原点で代数的に交わっていること。行列式と破壊現象の美しい関係など。
大学レベルになれば、微積分、線形代数、微分方程式、複素解析をゼロ除算の成果で修正、補充して行く。複素解析学におけるローラン展開の学習以前でも形式的なローラン展開(負べき項を含む展開)の中心の値をゼロ除算で定義し、広範な応用を展開する。特に微分係数が正や負の無限大の時、微分係数をゼロと修正することによって、微分法の多くの公式や定理の表現が簡素化され、教科書の結構な記述の変更が要求される。媒介変数を含む多くの関数族は、ゼロ除算 算法で統一的な視点が与えられる。多くの公式の記述が簡単になり、修正される。
複素解析学においては 無限遠点はゼロで表現されると、コペルニクス的変更(無限とされていたのが実はゼロだった)を行い、極の概念を次のように変更する。極、特異点の定義は そのままであるが、それらの点の近傍で、限りなく無限の値に近づく値を位数まで込めて取るが、特異点では、ゼロ除算に言う、有限確定値をとるとする。その有限確定値のいろいろ幾何学な意味を学ぶ。古典的な鏡像の定説;原点の 原点を中心とする円の鏡像は無限遠点であるは、誤りであり、修正し、ゼロであると いろいろな根拠によって説明する。これら、無限遠点の考えの修正は、ユークリッド以来、我々の空間に対する認識の世界史上に置ける大きな変更であり、数学を越えた世界観の変更を意味している。― この文脈では天動説が地動説に変わった歴史上の事件が想起される。
ゼロ除算は 物理学を始め、広く自然科学や計算機科学への大きな影響が期待される。しかしながら、ゼロ除算の研究成果を教科書、学術書に遅滞なく取り入れていくことは、真智への愛、真理の追究の表現であり、四則演算が自由にできないとなれば、人類の名誉にも関わることである。ゼロ除算の発見は 日本の世界に置ける顕著な貢献として世界史に記録されるだろう。研究と活用の推進を 大きな夢を懐きながら 要請したい。
以 上
追記:
(2016) Matrices and Division by Zero z/0 = 0. Advances in Linear Algebra & Matrix Theory, 6, 51-58.
http://www.diogenes.bg/ijam/contents/2014-27-2/9/9.pdfDOI:10.12732/ijam.v27i2.9.